How Medications Affect Magnesium Levels (and What to Know)
https://magtein.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/11/Screenshot-2025-11-08-at-3.50.15-PM.png 614 420 Riley Forbes Riley Forbes https://secure.gravatar.com/avatar/3f6c9bbe830133d8a02b6d78dd24a6cf57f35765554b3106fa7c0bce0d8772aa?s=96&d=mm&r=gThe Overlooked Link Between Medications and Nutrient Balance
Magnesium is a cornerstone mineral for health, essential for more than 600 enzymatic reactions in the human body. It plays a role in energy metabolism, cardiovascular function, stress response, and sleep regulation. However, magnesium balance can be disrupted by a variety of factors – including certain commonly used medications.
Long-term or frequent medication use can subtly deplete magnesium levels over time. Understanding which medications influence magnesium metabolism helps you take proactive steps to maintain balance and support overall wellness.*

Why Magnesium Depletion Occurs
Magnesium levels in the body are regulated through absorption in the gut, storage in bones and cells, and excretion through the kidneys. Some medications interfere with one or more of these processes – either by reducing absorption, increasing urinary loss, or altering how magnesium is distributed within tissues.
Because magnesium supports nerve transmission, muscle relaxation, and energy production, even mild depletion can affect how you feel daily. Over time, suboptimal levels may contribute to fatigue, muscle cramps, irritability, and difficulty sleeping.*
Who’s Most at Risk for Magnesium Depletion from Medications
Not everyone experiences the same degree of magnesium loss from medications. Certain populations may be more susceptible due to differences in metabolism, lifestyle, or overall health status.
Those most at risk include:
- Older adults: Magnesium absorption efficiency naturally declines with age, and many older adults take multiple medications that compound this effect.
- Individuals with digestive disorders: Conditions like celiac disease, inflammatory bowel disease, or chronic diarrhea can reduce magnesium uptake in the intestine.
- People under chronic stress: Elevated cortisol levels increase urinary magnesium losses and may amplify medication-related depletion.
- Athletes or individuals with high sweat output: Since magnesium is lost through perspiration, those with active lifestyles may have lower baseline reserves.
- Individuals on long-term prescriptions: Continuous use of medications like diuretics or PPIs increases the cumulative effect on magnesium balance over time.*
Recognizing these factors allows for more targeted monitoring and prevention strategies.*
Medications That May Lower Magnesium Levels
1. Diuretics (Water Pills)
Loop and thiazide diuretics, often prescribed for high blood pressure or heart failure, increase magnesium loss through urine. When magnesium excretion rises, serum levels can gradually decline. Combining magnesium-rich foods or supplementation may help maintain balance under medical supervision.*
2. Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs)
PPIs – commonly used for acid reflux and GERD – reduce stomach acidity, which impairs magnesium absorption in the intestine. Chronic PPI use has been associated with low serum magnesium levels, especially in older adults or those taking other magnesium-depleting medications.*
3. Certain Antibiotics
Medications in the aminoglycoside and macrolide classes can interfere with kidney reabsorption of magnesium, increasing losses through the urine. This effect typically appears with prolonged or high-dose antibiotic use.*
4. Oral Contraceptives and Hormone Therapies
Estrogen-containing medications influence magnesium utilization and retention. Some studies suggest that women taking oral contraceptives may have lower magnesium concentrations, which could affect mood stability or muscle tension over time.*
5. Chemotherapy Agents
Certain cancer therapies, such as cisplatin, can significantly deplete magnesium by damaging renal tubular cells. Patients receiving these treatments often require close monitoring of magnesium and other electrolytes to maintain balance.*
6. Insulin and Blood Sugar-Lowering Medications
Magnesium plays an essential role in glucose metabolism. Some insulin therapies and glucose-lowering drugs influence magnesium uptake in cells, contributing to fluctuations in magnesium status. Maintaining balanced magnesium levels helps support metabolic health and insulin sensitivity.*

How to Support Magnesium Balance While Taking Medications
The good news is that nutrient balance can be maintained with intentional strategies. Consider the following evidence-based steps:
1. Monitor Your Magnesium Status
If you take any long-term medications, ask your healthcare provider about periodic magnesium testing – especially if you experience fatigue, muscle weakness, or sleep disturbances.
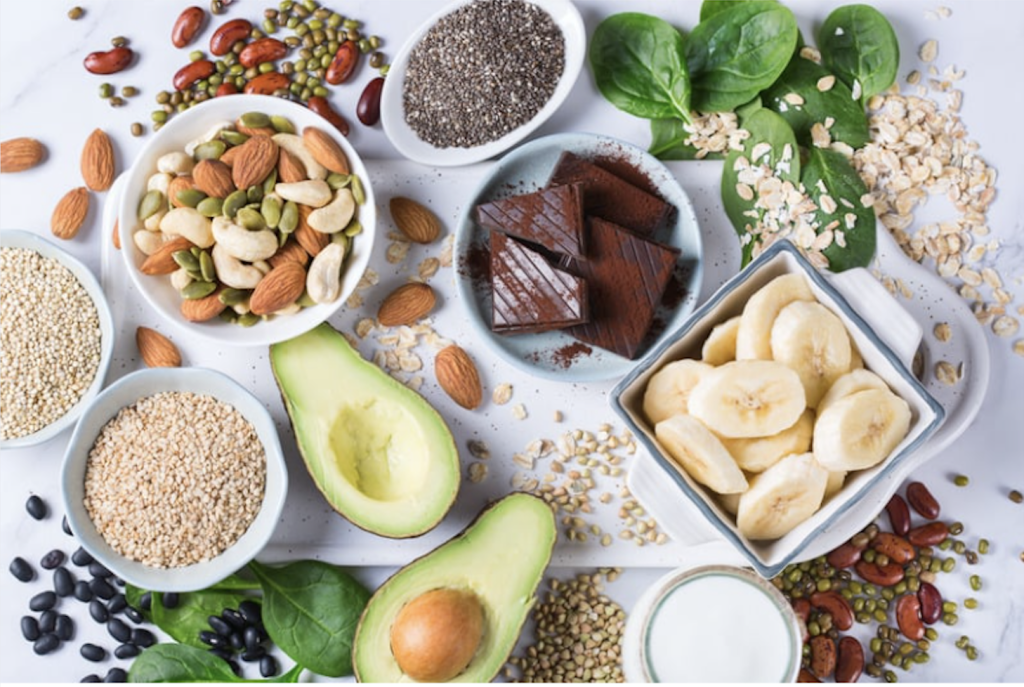
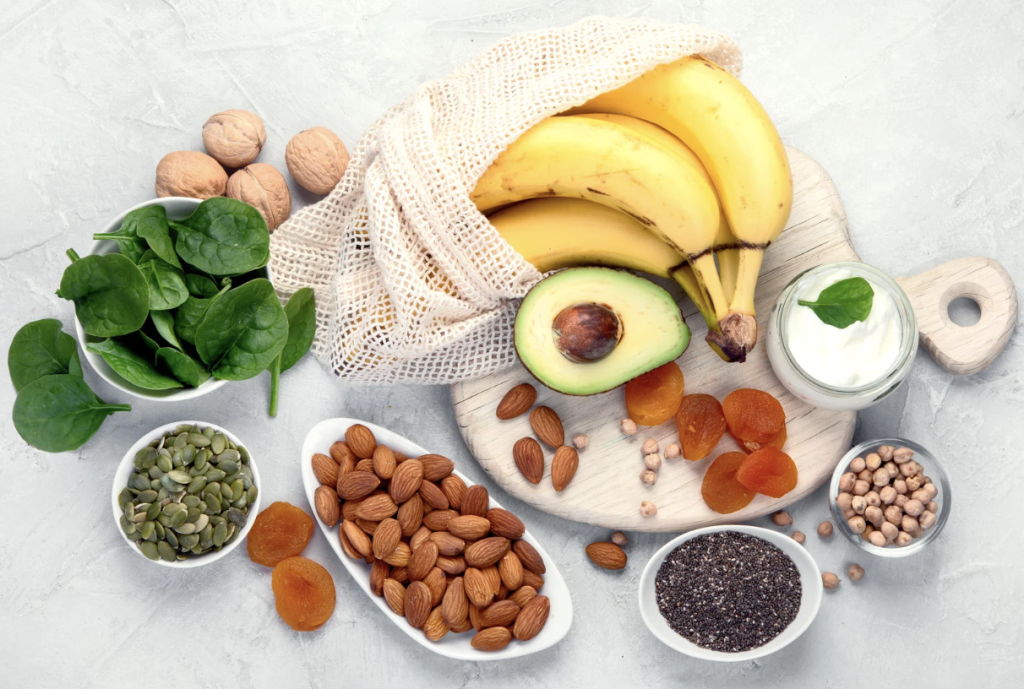
2. Focus on Magnesium-Rich Foods
Include leafy greens, nuts, seeds, legumes, avocados, and dark chocolate regularly. These whole foods not only provide magnesium but also supply cofactors such as vitamin B6 and antioxidants that support absorption.*
3. Consider Clinically Studied Supplementation
For individuals with higher magnesium demands, supplementation can help restore balance. Magtein® (magnesium L-threonate) offers a unique advantage – it effectively crosses the blood–brain barrier, supporting not only magnesium levels but also focus, memory, and mood regulation.*
4. Stay Hydrated and Balanced
Because magnesium works closely with other electrolytes – such as potassium and calcium – maintaining proper hydration and balanced nutrition is essential.
5. Collaborate With Your Healthcare Provider
Always discuss any supplements or dietary changes with your practitioner, particularly if you take prescription medications. Personalized guidance ensures safety and effective nutrient management.*
The Bottom Line
Medication-induced magnesium depletion is common but often overlooked. Because magnesium supports muscle, nerve, and brain function, maintaining healthy levels is key to overall vitality. Through mindful nutrition, consistent hydration, and evidence-based supplementation, it’s possible to restore balance and support long-term well-being – even while taking necessary medications.*

References
- Gröber U, Schmidt J, Kisters K. Magnesium in Prevention and Therapy. Nutrients. 2015;7(9):8199–8226.
- Markovits N, Loebstein R, Halkin H, et al. Proton pump inhibitors-induced hypomagnesemia: A new challenge. Drug Saf. 2014;37(5):391–403.
- Firoz M, Graber M. Bioavailability of US commercial magnesium preparations. Magnes Res. 2001;14(4):257–262.
- Guo X, et al. Association between diuretic use and magnesium deficiency: Evidence from clinical and experimental studies. Nutrients. 2022;14(4):811–823.
- National Institutes of Health. Magnesium – Fact Sheet for Health Professionals. https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Magnesium-HealthProfessional/. Accessed 2025.
These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. This product is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease.